Changing from one size of tire to another is a relatively complex operation and is not always possible.
It must confort the vehicles manufacturer’s recommendations and the local regulations.
For this reason we have listed below a series of fleet managers considerations to help our technical and commercial personnel advise clients on the compatibility of tire sizes.
Before changing the size of tire fitted the following points regarding both the tire and the vehicle should be checked:
LOAD CAPACITY
The load capacity of the replacement tire should not be inferior to that of the original tire, or at least it should be compatible with the maximum loads homologated for the vehicle in question.
SPEED
The speed code of the replacement tire must correspond to the maximum speed of the vehicle.
In some countries it is sufficient to respect the maximum speed imposed by the governor.
EXTERNAL DIAMETER OF tire
Every vehicle is designed for a certain tire size.
In order not to impare the performance of the vehicle the tire sizes should only vary within certain limits.
The increase or decrease in the diameter of the tire leads to a corresponding variation in the rolling circumference, which can affect both the vehicle height and vehicle speedometer and tachograph.
The permitted variation is of ± 5%.
WHEEL RIMS
Check that the new tire can be fitted to the existing wheel rims (consult the “Technical Data” booklet). If not, replace the rims.
SIZE
It is important to check that the tire and the wheel do not foul any part of the bodywork or the mechanical components of the vehicle at full articulation of the wheel. Furthermore, the tire must not protrude from the vehicle, or exceed local vehicle width regulations.
The minimum clearances that should in general be respected are as follows:
vertical space, that is the distance between the top of the tire and the wheelarch, this must be for a fully laden vehicle = 70/80 mm.
lateral space, that is, the distance between the sidewalls of the tire and the closest part of the vehicle:
fixed components (springs, spring hangers, brake arms), in this case the minimum distance should be 15 mm.
Mobile components (coachwork, mudguards, steering arms), in this case the minimum distance should be 50 mm.
The steering wheels should be checked on full lock.
Wheel to brake drum space, that is the distance separating the wheel and the brake drum.
The wheel must revolve freely and allow the brake drum to be ventilated.
The minimum distance should be at least 15 mm.
dual spacing for twinned tires, that is the distance separating the mid-points of twin tires.
The technical tables in the “Technical data” booklet should be checked for this information.
The distance between the twinned tires should be such that:
· it allows heat to be dispersed
· it avoids the trapping of foreign bodies between the tires which may cause damage.
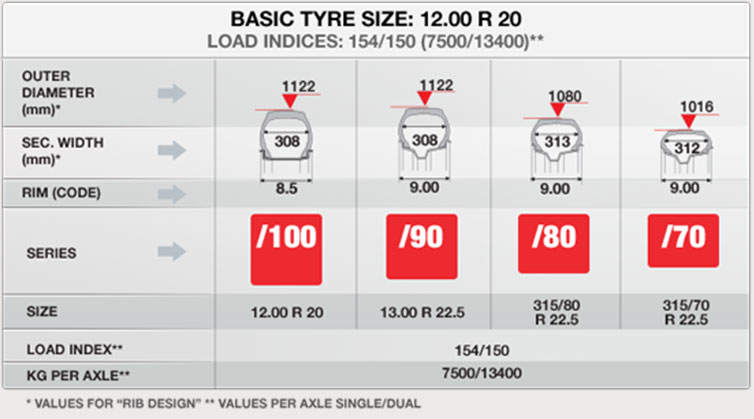
This section contains tables showing compatible loads for different tire sizes (at given axle loads).
It should be remembered that any change of tire size must respect all current legislation and the homologation specifications of the vehicle in question.
COMPATIBILITY IS CALCULATED ON THE BASIS OF THE LOADING CAPACITY.
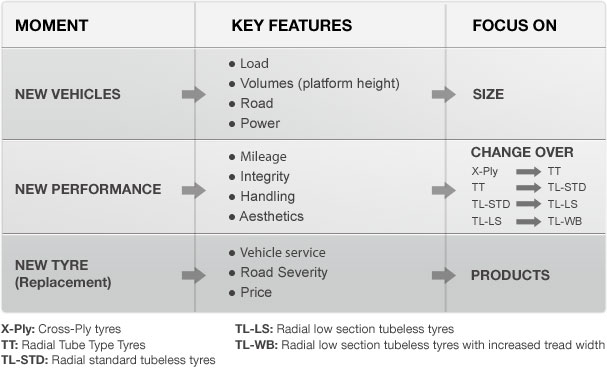
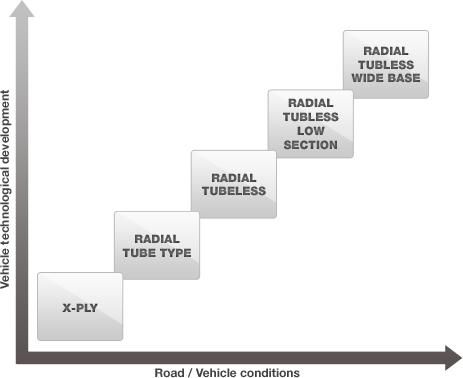
It is important to choose tires in relation to the use to which they will be put.
For long-distance transport low profile tires (/80 series) are advised whilst ultra-low profile tires (/70, /60 series) are suggested for volume transport.


 segment G
segment G  segment Q
segment Q  segment F
segment F